Sunday, May 9, 2021
Dynamic Arp Inspection , DAI
Tuesday, January 19, 2021
DHCP take 2
Now we will look at a larger topology with multiple switches, routers, portchannel and SVI interfaces to see how DHCP work.
Clients are connected VLAN101 on switches with Layer 2 functionality only, they are then connected with multiple connections creating a logical Layer2 portchannel interface between itself and the Layer3 switches (Port-Channel 1 for North-South connection, Port-Channel 2 diagonal connection). They are the first hop and run VRRP/HSRP for redundancy and they are further connected to routers which is the connection further where we have the actual DHCP servers.
Wednesday, December 30, 2020
DHCP take 1
You would think DHCP is easy, well it can be but it also can be quite tricky and sometimes it's a security risk you as the network administrator need to take care of.
I will start with a very small network to get the concepts straight and then I will do more complicated network and also add in the security layer.
Let's start with a small network, one switch with everything in same VLAN, a firewall, couple of servers and some clients (picture not showing all connected devices to the switch).
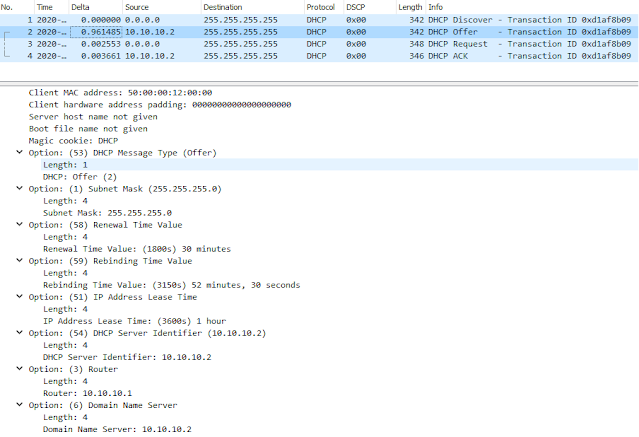
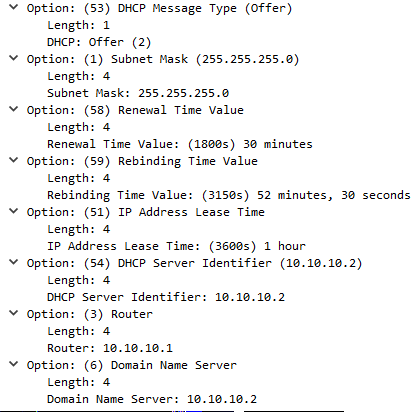
When client is connected to network (and is configured to get an DHCP assigned address) it will broadcast doing a DHCP Discover of a DHCP server. This discover will contain several parameters that client want to have offered to them, IP address is obvious but others such as default gateway, DNS servers etc..DHCP server will answer with a broadcast, DHCP Offer containing IP address and possibly other parameters.
If there are multiple DHCP servers answering the Discover client will pick one of them but usually the first Offer that it receives.
Client will then answer back with a broadcast DHCP Request to notify the second DHCP server that it will not take his offer but rather the first DHCP servers Offer, info about which offer to use is in the DHCP Requst packet even though its a broadcast.
The second DHCP server will see this DHCP request and see its not for him so he simply set the offered IP address as free in its DHCP database.
The first DHCP server will see the DHCP Request and write the offer into its DHCP database as assigned to client and also respond back to client with DHCP Ack.
A simple thing to memorize the process is to remember DORA, Discovery, Offer, Request, Ack.
Packets towards DHCP server is from UDP port 68 to port 67 and packets from server to client is the reverse, UDP from port 67 to port 68.
Friday, November 6, 2020
New focus
It has been long time since I wrote anything on this blog. Short reason is that I have not had time (or taken the time) to do so.
For the people that know me I have switched focus to my second baby “networking” which now is my main focus.
The switchover has been a lot of hard work but in the process I also managed to get the CCIE certification in Route & Switch , now renamed to Enterprise Infrastructure Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert
I have some topics that I will write about in the future so stayed tuned for some articles on mostly Cisco networking stuff.
Tuesday, August 4, 2015
Exchange Web Access changes name again
Every since Exchange 5.0 introduced access to mailboxes via a webgui, its name has changed several times.
Latest namechange is from Outlook Web App to Outlook on the web.
New features in Outlook on the web
Why the name change ? Your guess is equally good as mine, but I like that I don’t need to educate users about a new URL. It’s still https://..../owa